Note
Clip Vector Data with GeoPandas#
Learn how to clip geometries to the boundary of a polygon geometry using GeoPandas.
The example below shows you how to clip a set of vector geometries to the spatial extent / shape of another vector object. Both sets of geometries must be opened with GeoPandas as GeoDataFrames and be in the same Coordinate Reference System (CRS) for the clip function in GeoPandas to work.
This example uses example data from geodatasets 'geoda.chicago-health' and 'geoda.groceries', alongside a custom rectangle geometry made with shapely and then turned into a GeoDataFrame.
Note
The object to be clipped will be clipped to the full extent of the clip object. If there are multiple polygons in clip object, the input data will be clipped to the total boundary of all polygons in clip object.
Import Packages#
To begin, import the needed packages.
[1]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import geopandas
from shapely.geometry import box
import geodatasets
Get or Create Example Data#
Below, the example GeoPandas data is imported and opened as a GeoDataFrame. Additionally, a polygon is created with shapely and then converted into a GeoDataFrame with the same CRS as the GeoPandas chicago dataset.
[2]:
chicago = geopandas.read_file(geodatasets.get_path("geoda.chicago_commpop"))
groceries = geopandas.read_file(geodatasets.get_path("geoda.groceries")).to_crs(chicago.crs)
# Create a subset of the chicago data that is just the South American continent
near_west_side = chicago[chicago["community"] == "NEAR WEST SIDE"]
# Create a custom polygon
polygon = box(-87.8, 41.90, -87.5, 42)
poly_gdf = geopandas.GeoDataFrame([1], geometry=[polygon], crs=chicago.crs)
ERROR 1: PROJ: proj_create_from_database: Open of /home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/geopandas/conda/latest/share/proj failed
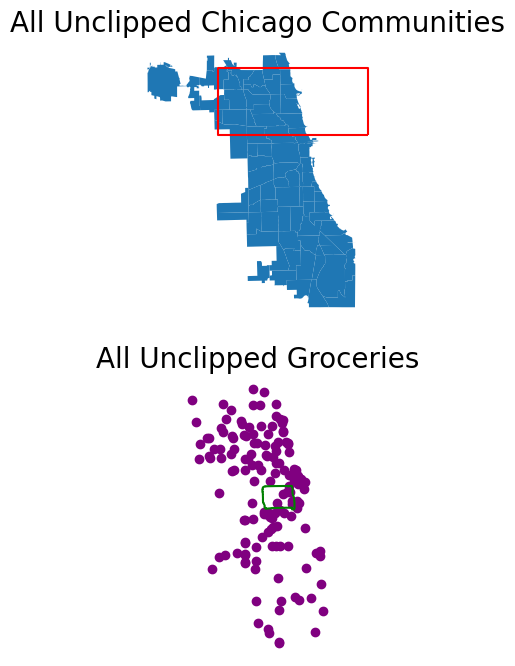
Plot the Unclipped Data#
[3]:
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(12, 8))
chicago.plot(ax=ax1)
poly_gdf.boundary.plot(ax=ax1, color="red")
near_west_side.boundary.plot(ax=ax2, color="green")
groceries.plot(ax=ax2, color="purple")
ax1.set_title("All Unclipped Chicago Communities", fontsize=20)
ax2.set_title("All Unclipped Groceries", fontsize=20)
ax1.set_axis_off()
ax2.set_axis_off()
plt.show()
Clip the Data#
The object on which you call clip is the object that will be clipped. The object you pass is the clip extent. The returned output will be a new clipped GeoDataframe. All of the attributes for each returned geometry will be retained when you clip.
Note
Recall that the data must be in the same CRS in order to use the clip method. If the data are not in the same CRS, be sure to use the GeoPandas GeoDataFrame.to_crs method to ensure both datasets are in the same CRS.
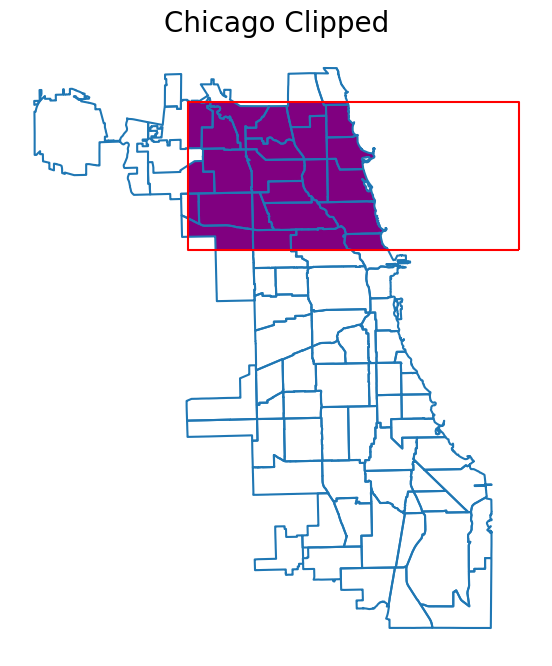
Clip the chicago Data#
[4]:
chicago_clipped = chicago.clip(polygon)
# Plot the clipped data
# The plot below shows the results of the clip function applied to the chicago
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 2
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 8))
chicago_clipped.plot(ax=ax, color="purple")
chicago.boundary.plot(ax=ax)
poly_gdf.boundary.plot(ax=ax, color="red")
ax.set_title("Chicago Clipped", fontsize=20)
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show()
Note
For historical reasons, the clip method is also available as a top-level function geopandas.clip. It is recommended to use the method as the function may be deprecated in the future.
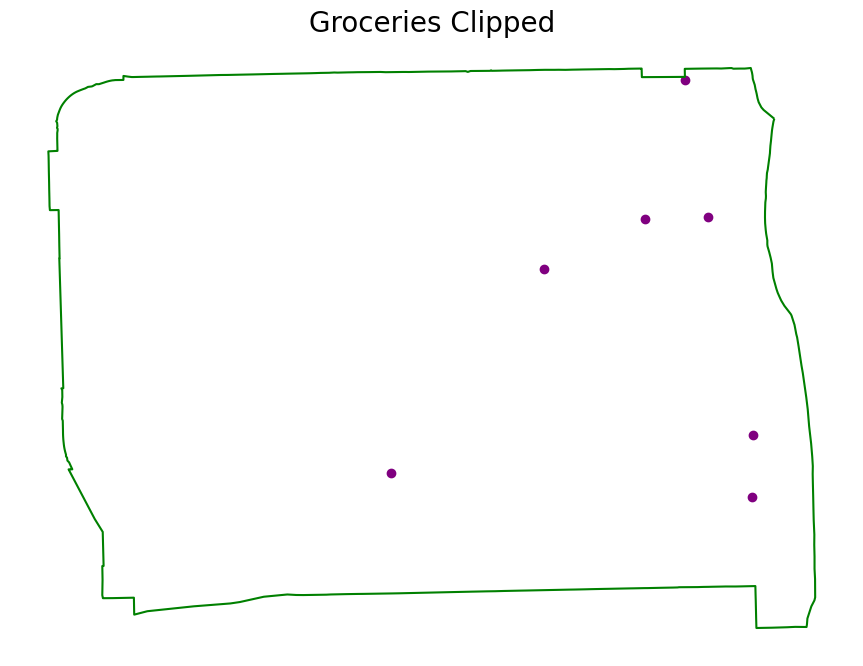
Clip the groceries Data#
[5]:
groceries_clipped = groceries.clip(near_west_side)
# Plot the clipped data
# The plot below shows the results of the clip function applied to the capital cities
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 8))
groceries_clipped.plot(ax=ax, color="purple")
near_west_side.boundary.plot(ax=ax, color="green")
ax.set_title("Groceries Clipped", fontsize=20)
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show()